The mountains of Nepal are murmuring winterly, and the sky is a fiery-white colour, and we are lured into the warmth by the cold, but the cold too is stealing some important article out of us, the sunshine vitamin. Vitamin d deficiency in winter becomes the silent friend of many, who hides behind the feeling of tiredness, sore muscles, and humorous changes in moods. This is one of the hidden dangers that should be known to remain healthy and lively during the cold months.
What Is Vitamin D and Why Does It Matter?
Vitamin D is no ordinary nutrient rather it is the answer to strong bones, good immunity and well being. However, this crucial vitamin is hard to come by during winter among most people.
Vitamin D, commonly referred to as a sunshine vitamin is essential in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus that make bones strong and prevent diseases such as osteoporosis. It is also involved in the functioning of the muscles, nerve conduction and immune well-being. Although vitamin D is also obtained in small quantities by the food that is eaten, the majority of it is synthesized by the skin when exposed to sunlight. During winter, the days are shorter and the sun is weak, which greatly decreases the amount of this natural production, posing a threat of vitamin D deficiency in winter.
The role of Vitamin D in bone and immune health
Vitamin D makes sure calcium and phosphorus are assimilated effectively making bones and teeth stronger. Weakened bones, fractures and general fatigue are some of the outcomes of a lack. In addition to the strength of muscles, vitamin D is beneficial to the immune system, which combats infections.
How sunlight helps your body produce Vitamin D
The sunlight contains UVB rays that turn a derivative of cholesterol in the skin into vitamin D3 the active form that your body may utilize. It is a natural process which is very slow during the winter especially in a region with high latitudes in the North or when there is a lot of pollution in the cloudy regions.
Why Vitamin D becomes harder to maintain during winter
Weather is cold, days are shorter and the lifestyles are indoor and hence reduced exposure to the sun. Winter clothes are also thick, which prevents UV rays. These compromising factors raise the occurrence rate of vitamin D deficiency in winter even among otherwise healthy adults.
Why Vitamin D Deficiency Increases in Winter
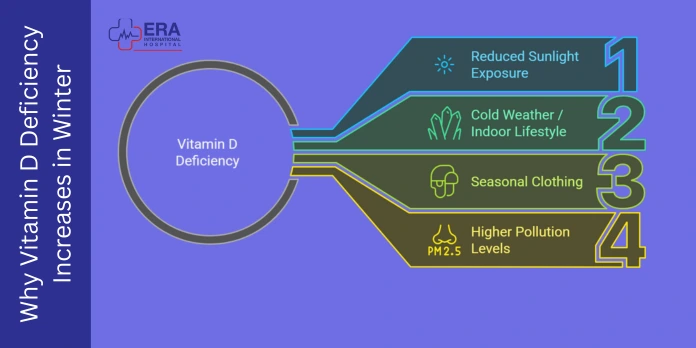
The change in the environment and lifestyle that occurs during winter forms an ideal storm against the loss of vitamin D. Knowing these reasons enables us to make preemptive action.
The lack of vitamin D during the winter is predisposed by a combination of several factors:
Reduced sunlight exposure due to shorter days
- The days during winter are shorter, and the sunlight is minimized.
- Human beings are spending more time in the house and they are lacking the daily 10-20 minutes of sunlight required to generate vitamin D.
Cold weather and indoor lifestyle patterns
- Fewer temperatures promote indoor activities.
- The heating systems can dry the skin and this can somewhat Vitamin D deficiency due to low production.
Seasonal clothing that blocks UV exposure
- Coats, scarfs and gloves restrict the exposure of the skin to sunlight.
Higher pollution levels affecting UV absorption
- The UVB rays can be filtered by air pollution, which reduces the production of vitamin D.
At-risk groups during winter
- Older people having a thinner skin.
- Individuals whose skin color is darker (greater melanin decreases the formation of vitamin D).
- Children confined indoors
- Desk employees who are not exposed to the sun much.
Common Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency in Winter
Vitamin D deficiency is hard to detect, with the symptoms appearing slowly. The initial step towards prevention is to know warning signs.
Vitamin D deficiency in winter usually does not show itself too much:
Early signs you shouldn’t ignore
- Persistent fatigue
- Generalized weakness
- Difficulty concentrating
How low vitamin D affects muscles and bones
- Skeletal pains, aches, and stiffness.
- Bone pain or stiffness
- Higher possibility of falls and fractures.
Mental health and mood changes linked to deficiency
- Deficiency of vitamin D may act as a cause of seasonal affective disorders (SAD).
- Major depression, irritability or minor depression.
Signs of severe or long-term deficiency
- Osteomalacia- softening of bones in adults.
- Rickets in children
- Weakened immunity or slow healing of wounds.
Health Risks Linked to Winter Vitamin D Deficiency
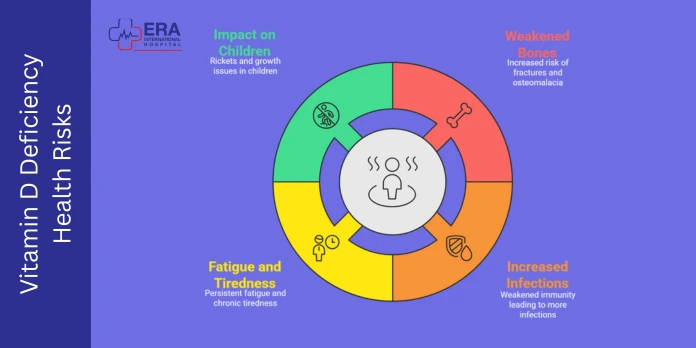
Deficiency that is not controlled may become severe health issues. These risks are most dangerous in winter when it is important to take control of them.
Weakened bones, fractures, and osteomalacia
- In adults, a long-term deficiency results in the weakening of bones, which provokes fractures.
Increased risk of infections due to weakened immunity
- Vitamin D promotes the immune system; the deficiency may increase the chances of colds, flu, and other infections.
Worsening fatigue and chronic tiredness
- Vitamin D deficiency inhibits energy generation and general vitality.
Impact on children (rickets, growth issues)
- Bones and skeletal defects are soft.
- Retarded growth and development.
Diagnosing Vitamin D Deficiency
Diagnosis Diagnosis is easy but necessary. Periodical testing will enable intervention to preclude complications.
When should you get tested?
- Constant bone/muscle achiness or tiredness.
- History of fractures
- Limited sunlight exposure
- Absorption-affecting chronic illness.
The 25-hydroxy Vitamin D blood test explained
- Routine blood test of vitamin D level.
- Deficiency, insufficiency or sufficiency are all determined by results.
Ideal Vitamin D levels and what they mean
- A range of 20-50 ng/mL is normally satisfactory.
- Any levels below 20 ng/ mL are deficient.
How to Prevent Vitamin D Deficiency in Winter
It would be better to prevent than to treat. It can be made up of simple everyday practices.
Safe sunlight exposure tips (even in cold weather)
- 10-20 minutes in the outdoor world each day.
- Hands and arms should face the sunlight where possible.
Vitamin-D-rich foods to include in your winter diet
- Fatty fish: sardines, mackerel, salmon.
- Egg yolks
- Exposure of mushrooms to sunlight.
Role of fortified foods and dairy products
- Vitamin D is usually added to milk, including plant-based milk, and cereals.
Are supplements necessary during winter?
- The supplement of vitamin D3 might be required, particularly in the case of indoor workers, aged people, and children.
Choosing between Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3
- D3 performs better in blood level elevation.
- D2 is a vegetarian alternative that is more weaker.
Lifestyle Habits That Support Healthy Vitamin D Levels

In addition to nutrition and sunshine, there are lifestyle practices which help in creating and absorbing vitamin D naturally.
Exercises that can be done outside during winter.
- Breathing open air, walking, jogging or light exercises.
- Minute sun flashes in broad daylight.
Benefits of exercise, mobility and circulation.
- Exercise assists in the use of calcium by bones.
- The immune system and good health.
The effect of sleep and stress on Vitamin D metabolism.
- Sleep deprivation and the continuous stress can lower the effectiveness of the vitamin D usage.
- The normal sleep patterns and stress management enhance results.
Special Focus: Vitamin D Deficiency in Nepal (Winter Context)
In Nepal, the local conditions play a great role in determining the level and extent of vitamin D deficiency during winter. Cities such as Kathmandu have a high rate of air pollution that may prevent UVB rays required in the production of vitamin D.
The winter haze also decreases the amount of sunlight that can reach the earth, therefore, many residents cannot obtain sufficient vitamin D through the process of natural production. This deficiency is also caused by dietary habits in Nepal.
Numerous individuals take too little fatty fish or fortified products, whereas the use of grains and vegetables is typically not enough to supply people with enough vitamin D. The combination of these factors leads to a general threat, especially that of some vulnerable populations.
In the winter, children spending the majority of their time inside a school, the elderly that are not very active, and those employees who work long hours in buildings without sun rays are particularly vulnerable to developing vitamin D deficiency. These local issues should be known to create the necessary intervention in time to preserve good health.
When to Seek Medical Care
The timely consultation with a doctor is also essential to preventing the development of long-term complications and to treat vitamin D deficiency during wintertime. The warning symptoms that should be taken into consideration are extreme pain in bones or bone fracture, exhaustion, muscle weakness, and frequent infections.
Although supplementation by vitamin D may be beneficial, self-supplementation is potentially dangerous. Overdose can cause toxicity, therefore it is always good to seek the advice of a medical practitioner to know what the right amount of the drug should be to the individual.
ERA International Hospital provides a full range of co-morbidity in diagnosis and treatment of deficiency. Proper blood testing reveals the levels of vitamin D and nutritional supplement plans, as well as diet and lifestyle therapy guarantee the sustainable change and healthy long-term results.
Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency during the winter is a usual occurrence which can be completely avoided with the appropriate strategy. It is possible to be aware of symptoms, lifestyle changes, and timely medical attention to ensure that one has strong bones, robust immunity and to be generally energetic in the colder months.
Safe outdoor time, including foods rich in vitamin D and fortified foods in the diet and supplementation in cases of insufficient sunlight exposure are all beneficial measures. Listening to such warning symptoms as fatigue, muscle pain, or depressed mood, and consulting a professional to do the tests and be treated makes sure that deficiency is controlled before it results in serious health complications.
These measures will ensure that people in Nepal avoid the risk of vitamin D deficiency during the winter and maintain their energy levels lively, their bones healthy, and their immunity robust during the winter.
FAQs:
How to increase vitamin D quickly?
Safe sunlight exposure, foods that contain vitamin D, and supplements are effective in increasing the amount of vitamin D within a short period of time. Spending 10-20 minutes outside a day is also helpful to people with the problem of vitamin D deficiency during winter. Foods such as fatty fish, egg yolks and fortified foods also aid the quick improvement. Pacific IVF recommends patients to add diet, supplements and lifestyle modifications to effectively treat the problem of vitamin D deficiency during winter. Regular checking makes sure the level of vitamin D is restored back to normal.
How to correct vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency in winter is a serious issue that needs a specific strategy in terms of the supplements, dietary changes, and regulated exposure to the sunlight. Pacific IVF may suggest that blood tests are regularly done to monitor progress when treating deficiency. A combination of these measures can be used to replenish a deficient vitamin D, and minimize winter-related symptoms of vitamin D deficiency. Early correction enhances the bone health, immunity and well being.
What blocks vitamin D absorption?
Various factors may inhibit the absorption of vitamin D and aggravate vitamin D deficiency during winter. The absorption can be lowered by conditions of the liver, kidneys, or the intestines, obesity, and even certain drugs. Poor dieting and the absence of sunlight also play a role. In Pacific IVF, patients are instructed to find out what hinders the absorption of vitamin D, so that the effects of prolonged deficiency of vitamin D during the winter period can be prevented.
What is a normal vitamin D level?
Normal levels of vitamin D are 20-50 ng/mL although the best levels are dependent on age and health. Vitamin D deficiency in winter can lead people to fall below this range and they may need to be taken as supplements. Pacific IVF focuses on the regular observation to ensure a healthy level and avoid complications of the deficient vitamin D level in winter. Normal levels of vitamin D promote health bones, immunity and wellness.


